Areas of Interest:
Deconstructing the role of the anterior midcingulate cortex (MCC) in goal-directed behaviour A central aim of my research program is to explain how reward-related MCC activity, as measured by the reward positivity, gives rise to various goal-directed behaviors (e.g. effort, adaptive decision-making, goal pursuit). Further, although studies of the reward positivity provide valuable insights into neural response patterns of MCC activity during reward processing, one cannot use correlative evidence from neuroimaging data to make causal inferences about the behavioral significance of the observed brain response. Because transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) offers a powerful tool for investigating causal brain-behavior relations, its experimental application may help reconcile or dispute theories of MCC function, thereby providing a deeper understanding of the functional significance of the reward positivity.
Recovery of reward function in substance use disorders. The cardinal feature of substance use disorders (SUD) – continued drug consumption despite its long-term adverse consequences – is indicative of abnormal goal-directed processes (e.g. control, reward valuation, decision-making). The long-term goal of my clinical research program is to reduce the frequency and severity of reward-related deficits among substance use disorders (SUDs). It is my hope that achieving this goal may ultimately increase substance users' control over drug use and maintaining treatment goals. To accomplish this goal, my current objective is to counteract the aberrant reward and decision-making processes observed in SUD by restoring the reward function of the MCC using TMS.
Understanding how humans travel from Point A to Point B A central aim of my current research program is to integrate experimental, computational, and theoretical analyses of spatial navigation in animals within the field of human EEG research. Key to this research direction was the discovery of an oscillatory component called right-posterior theta (RPT: 4-8 Hz). RPT describes a pattern of phase reset and power enhancement in right-posterior electrodes found to be sensitive to the spatial position of salient cues (e.g. rewards) during virtual navigation, and associated to spatial ability and memory. We are currently examining the role of RPT phase (peak vs trough) in memory encoding and retrieval with our closed-loop EEG-TMS system, and PHC navigational role in threat escape. If successful, this program will provide a pathway for altering the PHC function in memory-related disorders (e.g. dementia, trauma, Alzheimer’s disease, TBI, obesity) with the potential to enhance memory in general.
Behavioral and computational explorations of decision-making. Extensive empirical and computational work suggest that dopaminergic reward prediction error (RPE) signaling in the basal-ganglia facilitates or suppresses action representations in prefrontal cortex during reinforcement learning tasks: Phasic bursts of dopamine activity (positive RPEs) facilitate reward learning, whereas phasic dips in dopamine activity (negative RPEs) facilitate avoidance learning. My research has used the probabilistic selection task (PST), where subjects learn by trial-and-error to choose the ‘Good’ stimuli and avoid the ‘Bad’ ones, to assess how these mechanisms underlie individual differences in decision-making and relate to psychopathology. Computationally, I have used a standard reinforcement learning model known as Q-learning to simulate individual trial-to-trial task choices to compute learning rates for positive and negative RPE signals.
Special populations. Chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment (CCI) is a syndrome caused by the toxicity of chemotherapy agents in the brain. Although largely studied in adults, little is known on how these agents impact the developing brain. In collaboration with Dr. Peter Cole (Director of Pediatric Oncology, Rutgers Institute of Cancer), the goal of this research is to identify and validate the extent to which systemic chemotherapy may cause specific neurocognitive deficits in pediatric survivors. The long-term goal of this project is to improve care for CCI-related symptoms across the lifespan.
Tools of the Trade
- Smartmove robotic TMS system
- Magventure x100 TMS system
- Four Brainvision EEG amplifiers, acticaps, portable EEG rig including wireless triggering, recording and analysis software
- multiple HTCvive virtual reality systems
- Two Hololens Augmented Reality System
- Eyelink eyetracker system
- Soundproof chamber for EEG recording
- closed-loop EEG-TMS system
- EEG-MRI EGI system
- RUBIC imaging center one floor below the lab (https://rubic.rutgers.edu/) and 256 channel MRI compatible Hydrocel Geodesic Sensor EEG Net
- old school EEG machine from GRASS Instruments (coffee table now but see it in action here)
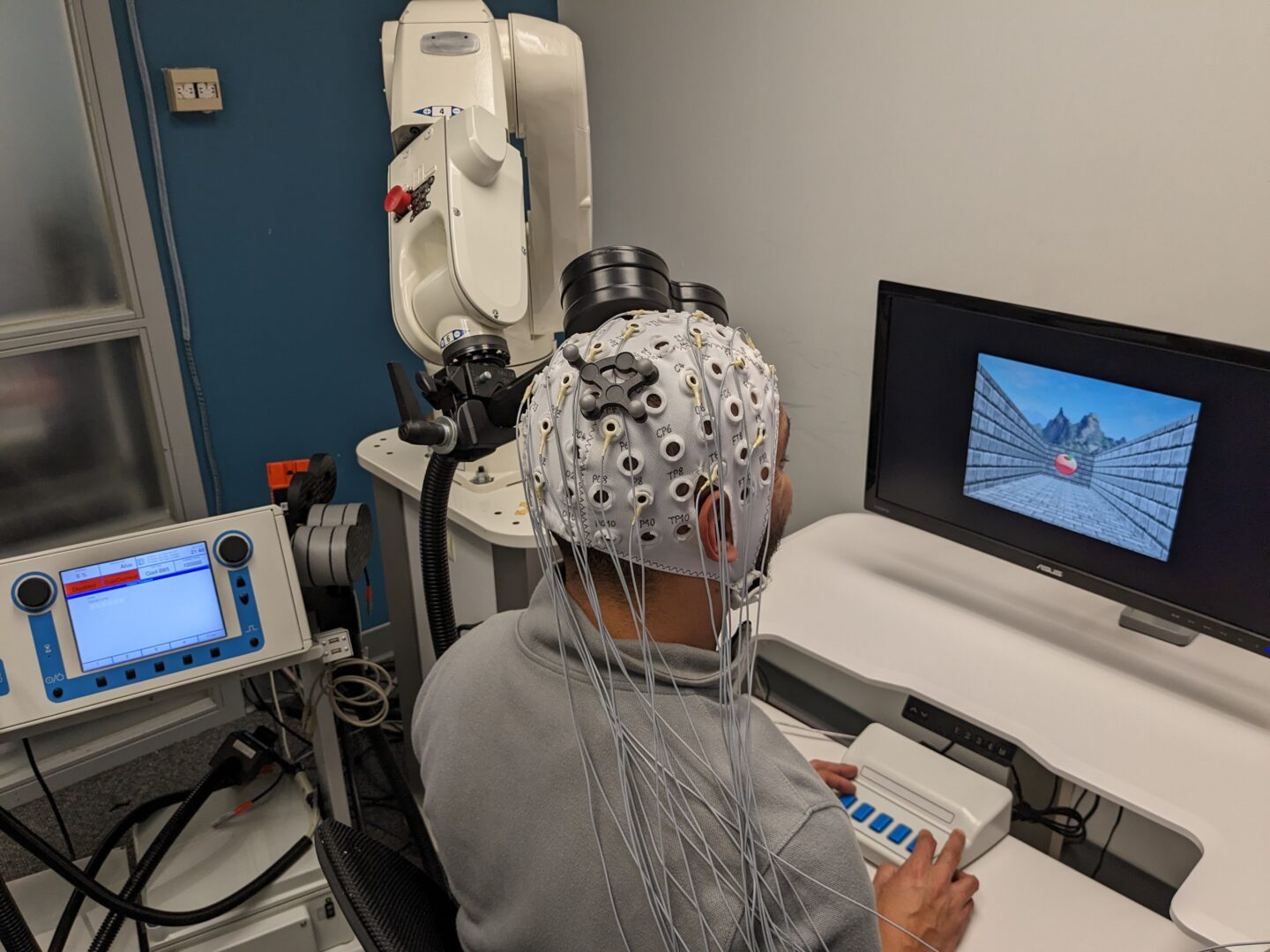
Robot-assisted Image-Guided Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Ri-TMS) enables several novel features for TMS research and treatment (e.g. exact targeting, motion compensation, precise continuation of the stimulation across consecutive sessions, multi-site targeting, and controlled coil movement over the scalp during stimulation). One goal of the lab is to identify optimal brain stimulation parameters (targeting site, pulse frequency) for modulating brain activity during goal-directed navigation in both health and disease.
Closed-Loop EEG-TMS Testing whether neural activity can be regulated through TMS in real-time. Our proposed method allows nearly instantaneous signal analysis and conditional TMS pulse delivery, providing unprecedented control to precisely coordinate TMS pulses based on phase and amplitude of cortical oscillation in real-time during goal-directed task performance (work in progress).


Virtual and Augmented Reality and EEG. The combined use of virtual reality and EEG to study neural mechanisms underlying goal-directed navigation. EEG combined with VR makes it possible to correlate humans’ electrophysiological signals with their every single movement in the designed environment.